Enterprises are rapidly moving beyond public AI technologies as data privacy, compliance, and intellectual property threats mount. Enterprise private LLM systems, which offer organisations more control over the deployment, governance, and scaling of AI models, have become more popular as a result of this change.
However, creating the ideal private LLM architecture is just as important to an enterprise’s success as selecting the appropriate model. Security limits, performance, cost effectiveness, and long-term ownership are all determined by architectural choices. Businesses now have a variety of deployment options, ranging from purely on-premise deployments to VPC and hybrid models.
Building safe, compliant, and production-ready AI systems requires an understanding of how Private LLM infrastructure functions across various models.
Why Private LLM Architecture Matters for Enterprises
Private LLM for enterprises is no longer a possibility for regulated and IP-sensitive organisations. Proprietary data is never allowed to escape protected areas thanks to an enterprise private LLM. But in the end, data control, security, and compliance are determined by architecture rather than model selection.
Structural constraints including shared infrastructure, opaque data management, and restricted auditability plague public LLMs. Scalability, GPU utilisation, and cost predictability are all directly impacted by a well-designed private LLM architecture. Additionally, it makes policy enforcement, logging, and governance possible across AI workflows.
Businesses that make early investments in the appropriate private LLM infrastructure benefit from improved performance tuning, long-term AI ownership, and the capacity to adapt their systems to changing business and regulatory needs.
For more details, read this.
What is Private LLM Architecture?
The full technical infrastructure that allows businesses to implement, oversee, and regulate massive language models in controlled settings is referred to as private LLM architecture. A private LLM for businesses entails ownership of inference pipelines, data flows, and security controls as opposed to merely using an API.
Architecture serves as a bridge between model ownership and model access, which are frequently misconstrued. Models operate where company data is located, not the other way around, thanks to an enterprise private LLM architecture. This method turns AI from a tool for experimentation into infrastructure fit for production.
Private LLM infrastructure provides uniform performance, compliance, and scalability across organisational use cases by specifying compute layers, data integration, security, and lifecycle management.
Core Components of a Private LLM Infrastructure
A strong private LLM infrastructure is made up of a number of interconnected parts. The model hosting and inference layer, which supports both task-specific SLMs and massive language models, is at the centre. Resource distribution in bare metal, virtualised, or elastic settings is managed by GPU and compute orchestration.
Enterprise systems, vector databases, and RAG pipelines are all securely connected by the data layer. Identity, access control, encryption, logging, and observability are all fundamental components of security.
Lastly, training, versioning, updates, and rollback are managed via MLOps and governance. These components work together to create a scalable private LLM architecture that enables an enterprise private LLM to function dependably in actual business settings.
An Explanation of Private LLM Deployment Models
Businesses can select from a variety of private LLM deployment methods, each with unique trade-offs. Operational ownership, latency, and security boundaries are all impacted by the selected paradigm. While some businesses prioritise complete isolation, others focus on speed and flexibility. Cost structures, from capital-intensive investments to usage-based models, are also impacted by deployment decisions.
For businesses, a private LLM must be in line with their long-term AI strategy, internal capabilities, and compliance requirements. The deployment model specifies how the private LLM architecture is translated into daily operations, whether it is on-premise, VPC-based, or hybrid. Before committing to an enterprise private LLM rollout, it is essential to comprehend these distinctions.
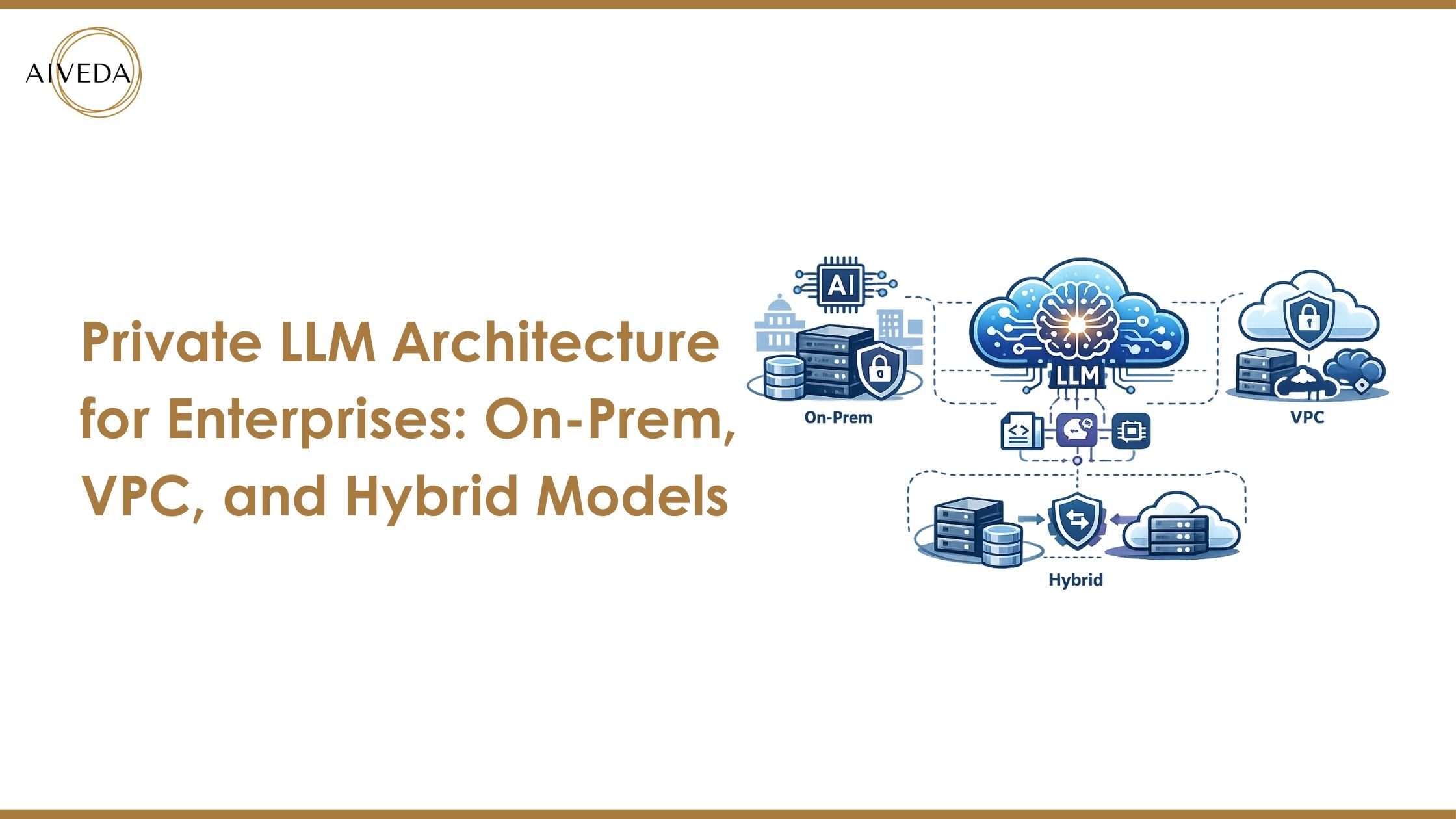
On-Premise Private LLM Architecture
How On-Prem LLM Deployment Works
The physical infrastructure of an organisation is where an enterprise private LLM operates. Training and inference are handled by dedicated on-premise GPUs, frequently in network contexts that are restricted or air-gapped. Businesses have complete control over data, models, and system behaviour with an on-premise LLM deployment. It is perfect for delicate tasks because no external connectivity is needed. Updates, monitoring, and scalability of the private LLM architecture are handled internally. Despite requiring a lot of resources, this method provides organisations with stringent compliance needs with unparalleled control and predictability.
Benefits of On-Premise Private LLMs
On-premise private LLM for enterprises delivers maximum data sovereignty and regulatory alignment. External exposure hazards are eliminated since data never exists on internal networks. Because resources are allocated to internal workloads, performance is predictable. Businesses obtain total control over their private LLM infrastructure, allowing for personalised governance and optimisation. Despite requiring a larger initial investment, this strategy offers a great return on investment for businesses with steady, long-term AI demand.
Challenges and Trade-Offs
Cost is the main obstacle to on-premise private LLM architecture. Large capital expenditures are needed for GPUs, cooling, and infrastructure. Elasticity is constrained and scaling is slower than with cloud-based models. Because internal teams have to handle MLOps, upgrades, and security, operational complexity rises. On-premise enterprise private LLM is only appropriate for companies with established AI operations due to these trade-offs.
Ideal Enterprise Use Cases
For businesses in the government, defence, healthcare, and BFSI sectors, on-premise private LLM is perfect. It works well for companies managing regulated datasets or extremely sensitive intellectual property. This design works best for businesses with steady, long-term AI workloads.
VPC-Based Private LLM Architecture
Deploying Private LLMs in a VPC Environment
A VPC-based private LLM operates in separate cloud networks with enterprise-grade restrictions. While integration with cloud security technologies makes management easier, private endpoints guarantee no exposure to the public internet. This private LLM architecture is well-liked by businesses updating their AI stack because it strikes a compromise between control and flexibility.
Private LLM on AWS VPC
IAM controls, managed GPU instances, and isolated networking are all utilised by a private LLM on AWS VPC. Businesses may maximise both cost and performance with autoscaling. AWS is appropriate for large-scale enterprise private LLM deployments due to its integration with enterprise data platforms.
Private LLM on Azure VNet
Strong monitoring, integrated compliance tools, and native identification using Azure AD are all advantages for a private LLM on Azure VNet. It fits in perfectly with Microsoft-focused private LLM for businesses.
Advantages and Limitations
Faster deployment and elastic scaling are made possible by VPC-based models. Businesses must, however, oversee shared accountability for cost control and security in their private LLM infrastructure.
Hybrid Private LLM Architecture
What a Hybrid LLM Deployment Looks Like
Cloud-based inference and on-premises data control are combined in a hybrid private LLM architecture. Sensitivity-based workload segmentation allows for dynamic scaling without complete reliance on the cloud. Large businesses are using this concept more and more.
Benefits of Hybrid Private LLM Architecture
Control and scalability are balanced in hybrid deployments. Cloud adoption occurs gradually, and GPU use is optimised. The most realistic enterprise private LLM strategy for many organisations is hybrid.
Common Hybrid Architecture Patterns
Sensitive versus non-sensitive workload separation, RAG pipelines across environments, and on-premises training with cloud inference are common themes.
Multi-Cloud Private LLM Architecture
Businesses may deploy and run an enterprise private LLM across several cloud providers while keeping tight control over data and governance thanks to a multi-cloud private LLM architecture. This strategy is frequently used to guarantee long-term AI flexibility and prevent vendor lock-in. Businesses can increase availability, resilience, and disaster recovery by dispersing private LLM infrastructure across clouds.
Nevertheless, architectural complexity is introduced by multi-cloud setups. Careful planning is required for data synchronisation, cross-cloud identity management, and policy enforcement. A multi-cloud strategy allows for workload optimisation and geographical compliance for private LLM for businesses with international operations. This architecture facilitates scalable AI growth, strategic independence, and company continuity when properly applied.
On-Prem vs VPC vs Hybrid: Private LLM Architecture Comparison
| Comparison Factory | On-Prem Private LLM | VPC-Based Private LLM | Hybrid Private LLM |
| Security & Compliance | Maximum control, full data sovereignty | Strong isolation with cloud security controls | High control with selective cloud exposure |
| Scalability & Performance | Limited elasticity, predictable performance | Highly elastic with autoscaling | Balanced scalability across environments |
| Cost & TCO | High upfront CAPEX, lower long-term variability | OPEX-based, requires cost governance | Optimized cost through workload distribution |
| Deployment Speed | Slow to deploy due to infrastructure setup | Faster deployment using cloud resources | Moderate, depends on integration complexity |
| Operational Complexity | High internal MLOps and infra management | Shared responsibility with the cloud provider | Higher complexity but greater flexibility |
| Best Fit For | Highly regulated, stable workloads | Cloud-ready enterprises need agility | Enterprises balancing control and scale |
How Enterprises Choose the Right Private LLM Architecture
Technical preference alone is not the only factor that influences the strategic choice of private LLM architecture. Businesses need to assess intellectual property threats, data sensitivity, and regulatory constraints.
Compared to experimental AI workloads, a private LLM for businesses managing client data or proprietary models could need more separation. Internal AI maturity is also important; companies with poor MLOps capabilities would favour hybrid or VPC installations.
Architecture choices should be influenced by long-term ROI, scalability requirements, and talent availability. Businesses can avoid later, expensive re-architecture by matching business objectives with private LLM infrastructure capabilities. An enterprise private LLM may stay safe, scalable, and compatible with future expansion with the correct architecture.
The Future of Enterprise Private LLM Infrastructure
Flexible, governance-first architectures are the way of the future for enterprise private LLM adoption. As businesses strike a balance between control and scalability, hybrid and multi-cloud configurations are increasingly the norm. In order to lower GPU costs and increase work efficiency, Small Language Models are likewise becoming more and more popular.
Businesses are giving policy-driven control, cost optimisation, and observability top priority as private LLM infrastructure develops. AI is now regarded as essential digital infrastructure rather than as a stand-alone tool. Designing systems that adapt to corporate needs, legislative changes, and model innovation while preserving long-term ownership and control will be essential to the success of private LLM for businesses.
Designing a Scalable and Secure Private LLM Architecture
A key business choice that directly affects security, performance, and AI ROI is a private LLM architecture. Businesses that approach architecture as a long-term strategy rather than a quick fix for deployment benefit from improved operational resilience and oversight.
Ownership of inference environments, data pipelines, and models guarantees the enterprise private LLM’s continued adaptability and compliance. Organisations can seamlessly incorporate new models, technologies, and workflows thanks to scalable design. Businesses can confidently increase the usage of AI across departments with the proper Private LLM infrastructure.